Synthesis and characterization of bacterial cellulose composite with graphite and TiO2-ZnO: structural and functional analysis
Authors
Muhammad Fariz Nafiir , Sudirman , Emmy Yuanita , Sazmal E. Arshad , Retno Ariadi Lusiana , Maria UlfaDOI:
10.29303/aca.v7i2.204Published:
2024-10-31Issue:
Vol. 7 No. 2 (2024)Keywords:
bacterial cellulose, graphite, TiO2-ZnO, composite, FTIR, SEM-EDS, conductivity, mechanical properties, swellingArticles
Downloads
How to Cite
Downloads
Metrics
Abstract
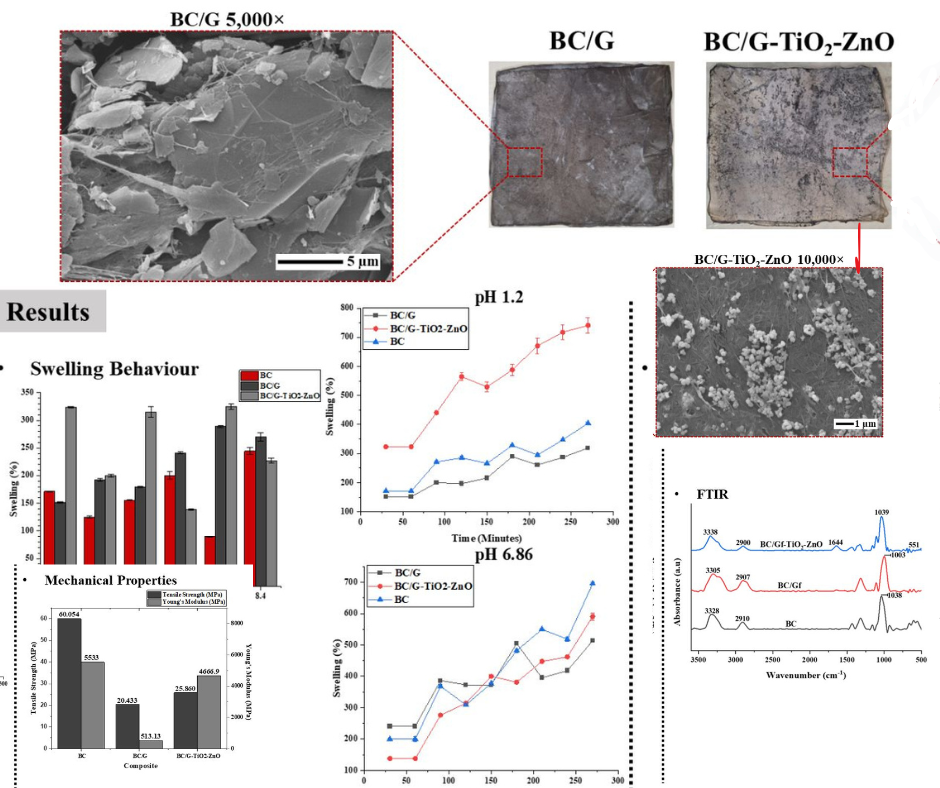
This research aims to synthesize and characterize a bacterial cellulose (BC)-based composite with graphite and TiO2-ZnO as reinforcement materials using ex-situ synthesis with CTAB as a surfactant. FTIR and SEM-EDS analysis revealed interactions between the matrix and the reinforcement materials, as well as irregular particle distribution in the BC/G-TiO2-ZnO composite. The addition of graphite to BC significantly increased the conductivity of the composite, while the addition of TiO2-ZnO had the opposite effect. The mechanical properties of the composite exhibited an inverse relationship with the conductivity parameter. Swelling tests indicated that pH and the addition of CTAB influenced the swelling behavior of the BC-based composite. The results of this study provide a strong foundation for the development of potential applications in the fields of electronics and pollutant filtration. The synthesis of this composite aims to harness the unique properties of BC, graphite, and TiO2-ZnO, creating a multifunctional material with potential uses in flexible electronics, sensors, biocompatible conductive materials, and advanced filtration systems.
References
Blomquist, N., Engstrom, A. C., Hummelgard, M., Andres, B., Forsberg, S., & Olin, H. (2016). Large-Scale Production of Nanographite by Tube-Shear Exfoliation in Water. Plos One, 1(1), 1-11.
Ulfa, M., Noviani, I., Yuanita, E., Dharmayani, N. K. T., Sudirman, & Sarkono. (2023). Synthesis and Characterization of Composites-Based Bacterial Cellulose by Ex-Situ Method as Separator Battery. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan IPA, 9(6), 4647-4651.
Choi, S. M., Rao, K. M., Zo, S. M., Shin, E. J., & Han, S. S. (2022). Bacterial Cellulose and Its Applications. Polymers, 14(1080), 1-44.
Zhong, C. (2020). Industrial-Scale Production and Applications of Bacterial Cellulose. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 8(605374), 1-19.
Gregory, D. A., Tripathi, L., Fricker, A. T., Asare, E., Orlando, I., Raghavendran, V., & Roy, I. (2021). Bacterial cellulose: A smart biomaterial with diverse applications. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 145, 100623.
Vilela, C., Pinto, R. J. B., Pinto, S., Marques, P., Silvestre, A., & Barros, C. S. D. R. F. (2018). Polysaccharide-based hybrid materials: metals and metal oxides, graphene, and carbon nanotubes. Springer.
Bodzek, M., Konieczny, K., & Kwiecińska-Mydlak, A. (2020). The application of nanomaterial adsorbents for the removal of impurities from water and wastewaters: a review. Desalination and Water Treatment, 185, 1-26.
Wahid, F., Zhao, X. Q., Cui, J. X., Wang, Y. Y., Wang, F. P., Jia, S. R., & Zhong, C. (2022). Fabrication of Bacterial Cellulose with TiO2-ZnO Nanocomposites as a Multifunctional Membrane for Water Remediation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 620(1), 1-13.
Jayanthi, S., Shenbagavalli, S., Muthuvinayagam, M., & Sundaresan, B. (2022). Effect of Nano TiO2 on The Transport, Structural and Thermal Properties of PEMA-NaI solid polymer electrolytes for Energy storage devices. Material Science Engineering: B, 285, 115942.
Ul-Islam, M., Khattak, W. A., Ullah, M. W., Khan, S., & Park, J. K. (2014) Synthesis of Regenerated Bacterial Cellulosa-Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite Films for Biomedical Applications. Cellulose, 21(1), 433-447.
Ramadhika, L. N., Aprilia, A., & Safriani, L. (2021). Studi Preparasi Senyawa ZnO: TiO2 Sebagai Material Fotokatalis. Jurnal Material dan Energi Indonesia, 11(2), 83-95.
Aritonang, H. F., Wulandari, R., & Wuntu, A. D. (2020). Synthesis and Characterization of Bacterial Cellulose/Nano-Graphite Nanocomposite Membranes. Macromolecular Symposia, 391(1900145), 1-7.
Al-arjan, W. S., Khan, M. U. A., Almutairi, H. H., Alharbi, S. M., & Razak, S. I. A. (2022). pH-Responsive PVA/BC-f-GO Dressing Material for Burn and Chronic Wound Healing with Curcumin Release Kinetics. Polymers, 14(1949), 1-16.
Susilo, B. D., Suryanto, H., & Aminuddin. (2021) Characterization of Bacterial Nanocellulose–Graphite Nanoplatelets Composite Films. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science and Technology, 5(2), 145-154.
Feng, Y., Zhang, X., Shen, Y., Yoshino, K., & Feng, W. (2012). A mechanically strong, flexible, conductive film based on bacterial cellulose/graphene nanocomposite. Carbohydrate polymers, 87(1), 644-649.
Zhu, C., Li, F., Zhou, X., Lin, L., & Zhang, T. (2014). Kombucha‐synthesized bacterial cellulose: Preparation, characterization, and biocompatibility evaluation. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 102(5), 1548-1557.
Czaja, W., Romanovicz, D., & Brown Jr, R. M. (2004). Structural investigations of microbial cellulose produced in stationary and agitated culture. Cellulose, 11(4), 403-411.
Ybañez, M. G., & Camacho, D. H. (2021). Designing hydrophobic bacterial cellulose film composites assisted by sound waves. RSC advances, 11(52), 32873-32883.
Mubari, P. K., Beguerie, T., Monthioux, M., Weiss-Hortala, E., Nzihou, A., & Puech, P. (2022). The X-ray, Raman, and TEM signatures of cellulose-derived carbons explained. C, 8(1), 4.
Annu, Bhat, Z. I., Imtiyaz, K., Rizvi, M. M. A., Ikram, S., & Shin, D. K. (2023). Comparative Study of ZnO-and-TiO2-Nanoparticles-Functionalized Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Bionanocomposites for Multifunctional Biomedical Applications. Polymers, 15(16), 3477.
Ali, H. A., & Hameed, N. J. (2022). Preparation of cellulose acetate nanocomposite films based on TiO2-ZnO nanoparticles modification as food packaging applications. Journal of Applied Sciences and Nanotechnology, 2(3), 115-125.
Cazan, C., Enesca, A., & Andronic, L. (2021). Synergic effect of TiO2 filler on the mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites. Polymers, 13(12), 2017.
Zhang, L., Yu, Y., Zheng, S., Zhong, L., & Xue, J. (2021). Preparation and properties of conductive bacterial cellulose-based graphene oxide-silver nanoparticles antibacterial dressing. Carbohydrate Polymers, 257, 117671.
Aditya, T., Allain, J. P., Jaramillo, C., & Restrepo, A. M. (2022). Surface modification of bacterial cellulose for biomedical applications. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(2), 610.
Ameh, T., Zarzosa, K., Dickinson, J., Braswell, W. E., & Sayes, C. M. (2023). Nanoparticle surface stabilizing agents influence antibacterial action. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, 1119550.
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Muhammad Fariz Nafiir, Sudirman, Emmy Yuanita, Sazmal E. Arshad, Retno Ariadi Lusiana, Maria Ulfa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license allows authors to use all articles, data sets, graphics, and appendices in data mining applications, search engines, web sites, blogs, and other platforms by providing an appropriate reference. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright without restrictions and will retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).





 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





