Design of heat exchanger for producing nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanoparticles using coprecipitation method
Penulis
Sifa Aulia Rahma , Asep Bayu Dani Nandiyanto , Teguh KurniawanDOI:
10.29303/aca.v6i2.144Diterbitkan:
2023-05-16Terbitan:
Vol 6 No 2 (2023)Kata Kunci:
Heat Exchanger (HE), Nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) , nanoparticles, Shell and tubeArticles
Unduhan
Cara Mengutip
Unduhan
Metrik
Abstrak
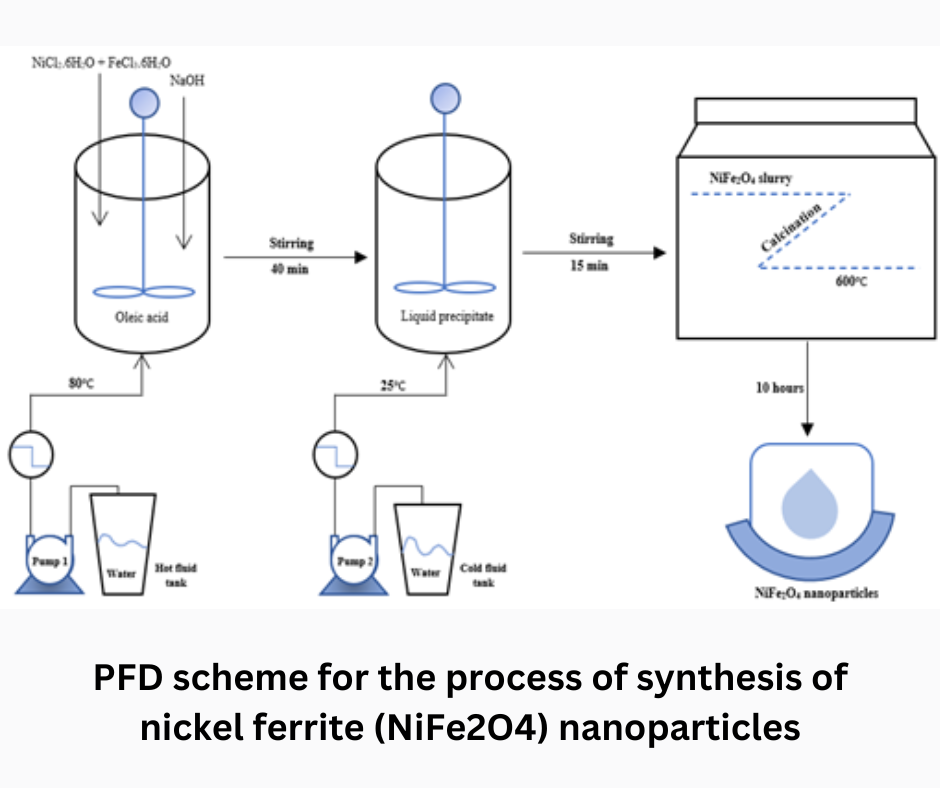
This study examines the design of a heat exchanger (HE) in the production process of nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanoparticles using the coprecipitation method by determining the shell and tube heat exchanger. The Microsoft Excel application is used as a manual calculating machine to facilitate the analysis of heat exchanger (HE) data calculations. The research flowchart starts with a literature study, preparation of tools and materials for design, calculation of the main shell and tube components, and then fabrication. Based on the calculation results, the design specification data for a shell and tube heat exchanger has a shell diameter of 0.032 m, a shell length of 4.267 mm, a thickness of 0.002 m with an initial heat transfer rate (Q) of 460130 W resulting in a heat transfer efficiency of 95.706% and an NTU of 6.165. The high effectiveness value makes the design of the one shell and tube type turbulent flow heat exchanger (HE) considered to have met the standards of high effectiveness and good performance. The design and design process is complete if the device functions properly. This study can be used as a reference for researchers in designing heat exchangers during production to make them more effective, reliable, and economical.
Referensi
Purnamasari, H. N., Kurniawan, T., & Nandiyanto, A. B. D. (2021). DESIGN OF SHELL AND TUBE TYPE HEAT EXCHANGER FOR NANOFIBRIL CELLULOSE PRODUCTION PROCESS. International Journal of Research and Applied Technology (INJURATECH), 1(2), 318-329.
Marawijaya, G., Trisnaliani, L., & Purna, C. (2019). Protoype Heat Exchanger Type Shell and Tube Ditinjau Dari Variasi Jarak Baffle Dan Laju Alir Massa Udara Panas. KINETIKA, 10(1), 18-23.
Ibrahim, H., Sazali, N., Shah, A. S. M., Karim, M. S. A., Aziz, F., & Salleh, W. N. W. (2019). A review on factors affecting heat transfer efficiency of nanofluids for application in plate heat exchanger. Journal of Advanced Research in Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences, 60(1), 144-154.
Than, S. T. M., Lin, K. A., & Mon, M. S. (2008). Heat exchanger design. world academy of science, engineering and technology, 46, 604-611.
Abou Elmaaty, T. M., Kabeel, A. E., & Mahgoub, M. (2017). Corrugated plate heat exchanger review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 70, 852-860.
Oh, C. H., Kim, E. S., & Patterson, M. (2010). Design option of heat exchanger for the next generation nuclear plant. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 132(3).
Magistri, L., Traverso, A., Massardo, A. F., & Shah, R. K. (2006). Heat exchangers for fuel cell and hybrid system applications.
Dagdas, A. (2007). Heat exchanger optimization for geothermal district heating systems: A fuel saving approach. Renewable Energy, 32(6), 1020-1032.
Selbaş, R., Kızılkan, Ö., & Reppich, M. (2006). A new design approach for shell-and-tube heat exchangers using genetic algorithms from economic point of view. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 45(4), 268-275.
Tiyaboonchai, W. (2013). Chitosan nanoparticles: a promising system for drug delivery. Naresuan University Journal: Science and Technology (NUJST), 11(3), 51-66.
Ozaki, M. (1989). Preparation and properties of well-defined magnetic particles. MRS bulletin, 14(12), 35-40.
Kooti, M., & Sedeh, A. N. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of NiFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles by combustion method. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 29(1), 34-38.
Malekfar, R., Parishani, M., & Cheraghi, A. (2015). Spectroscopy, Structural, and Optical Investigations of NiFe2O4 Ferrite. International Journal of Optics and Photonics, 9(2), 73-78.
Balakrishnan, P., & Veluchamy, P. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles using sol-gel method. Int J ChemTech Res, 8, 271-276.
Noorlela, A., Nandiyanto, A. B. D., Ragadhita, R., & Kurniawan, T. (2023). Design of reactor for the production of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Acta Chimica Asiana, 6(1), 254-262.
Maaz, K., Karim, S., Mumtaz, A., Hasanain, S. K., Liu, J., & Duan, J. L. (2009). Synthesis and magnetic characterization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by coprecipitation route. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 321(12), 1838-1842.
Nurmayansih, A., Hariani, P. L., & Said, M. (2021). Synthesis NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles by coprecipitation Method for Degradation of Congo Red Dye. IJFAC (Indonesian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Chemistry), 6(3), 115-121.
Sagadevan, S., Chowdhury, Z. Z., & Rafique, R. F. (2018). Preparation and characterization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles via coprecipitation method. Materials Research, 21.
Srivastava, M., Chaubey, S., & Ojha, A. K. (2009). Investigation on size dependent structural and magnetic behavior of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel and hydrothermal methods. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 118(1), 174-180.
Asri, N. S. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of Soft Magnetic Materials NixZn1-xFe2O4 (x = 0,2 – 0,8) Lombok Iron Sand with Coprecipitation Method. Journal of Technomaterial Physics, 3(1), 21-28.
Nurjanah, N., Adzkia, Q. A. A., Rustana, R., Carolline, S. C., Agustine, S. M., & Nandiyanto, A. B. D. (2022). A Review: Nanoparticles NiFe2O4 Synthesis and Its Application as Hyperthermia Agents in Biomedicine. Indonesian Journal of Chemical Science, 11(2), 103-113.
Lu, A. H., Salabas, E. E., & Schüth, F. (2007). Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 46(8), 1222-1244.
Jegede, F. O., & Polley, G. T. (1992). Optimum heat exchanger design. Transactions of the Institution of Chemical Engineers;(United Kingdom), 70(pt A).
Caputo, A. C., Pelagagge, P. M., & Salini, P. (2008). Heat exchanger design based on economic optimisation. Applied thermal engineering, 28(10), 1151-1159.
Guo, Z. Y., Liu, X. B., Tao, W. Q., & Shah, R. K. (2010). Effectiveness–thermal resistance method for heat exchanger design and analysis. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 53(13-14), 2877-2884.
Sengers, J. V., & Watson, J. T. R. (1986). Improved international formulations for the viscosity and thermal conductivity of water substance. Journal of physical and chemical reference data, 15(4), 1291-1314.
Nandiyanto, A. B. D., Putri, S. R., Ragadhita, R. I. S. T. I., & Kurniawan, T. E. G. U. H. (2022). Design of Heat Exchanger for the Production of Carbon Particles. J. Eng. Sci. Technol, 17(4), 2788-2798.
Shihab, F., Hadisantoso, E. P., & Setiadji, S. (2022, December). Sintesis dan Karakterisasi Nanokomposit ZnO/NiFe2O4 dari Limbah Baterai menggunakan Metode Solid State sebagai Fotokatalis Zat Warna Metilen Biru. In Gunung Djati Conference Series (Vol. 15, pp. 23-32).
Chen, J. C. (1966). Correlation for boiling heat transfer to saturated fluids in convective flow. Industrial & engineering chemistry process design and development, 5(3), 322-329
Lisensi
Hak Cipta (c) 2023 Sifa Aulia Rahma Sifa Aulia Rahma, Asep Bayu Dani Nandiyanto, Teguh Kurniawan

Artikel ini berlisensiCreative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license allows authors to use all articles, data sets, graphics, and appendices in data mining applications, search engines, web sites, blogs, and other platforms by providing an appropriate reference. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright without restrictions and will retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).





 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





