Network pharmacology and molecular docking simulation uncovered the potential of hexacyclinic acid as anti-osteoarthritis by regulating IL-17 signaling pathway
Authors
Arif SetiawansyahDOI:
10.29303/aca.v8i1.238Published:
2025-05-31Issue:
Vol. 8 No. 1 (2025)Keywords:
Hexacyclinic acid, Network pharmacology, Molecular docking, Osteoarthritis, IL-17 signaling pathwayArticles
Downloads
How to Cite
Downloads
Metrics
Abstract
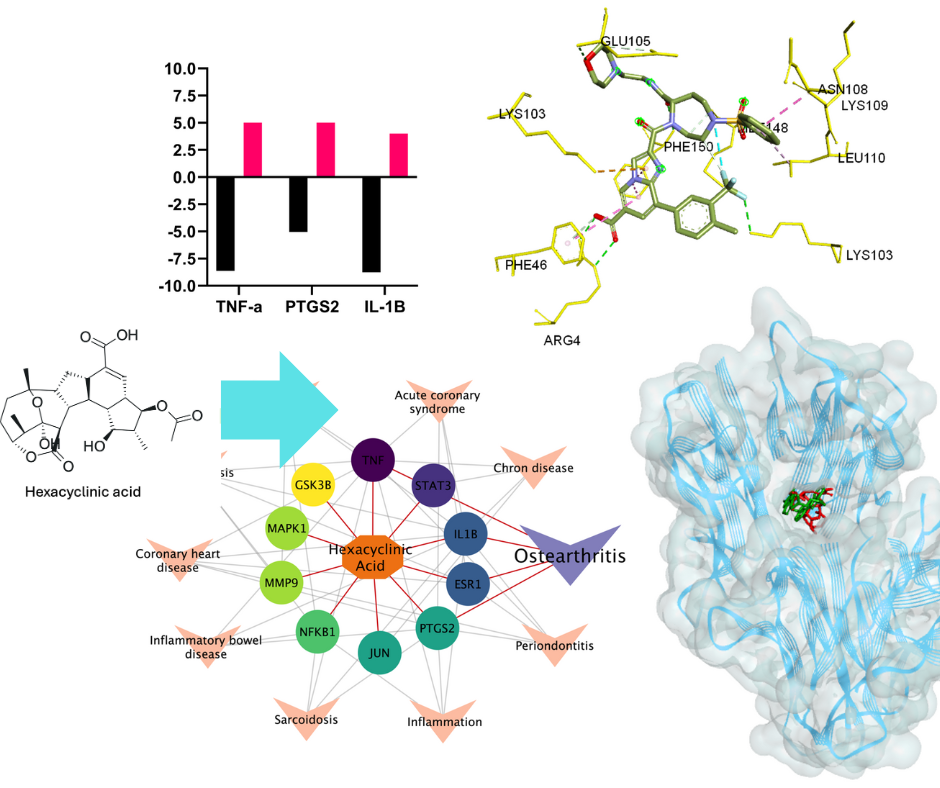
Hexacyclinic acid has shown promising pharmacological activities, yet its molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential remain largely unexplored. This study aimed to identify potential disease targets and elucidate the mechanism of action of hexacyclinic acid using an integrated computational approach. We employed network pharmacology analysis to predict potential targets and pathways of hexacyclinic acid using SuperPred and Swiss Target server, followed by protein-protein interaction network construction via STRING database. Pathway enrichment analysis was performed using ShyniGO and DAVID databases. Molecular docking studies were conducted using AutoDock Vina to evaluate binding affinities between hexacyclinic acid and identified target proteins. Binding poses and interactions were visualized using Biovia Discovery Studio Visualizer. Disease prediction analysis identified osteoarthritis as the most promising target, with the IL-17 signaling pathway emerging as the most significant KEGG pathway. TNF-α and IL-1β were identified as key molecular targets within this pathway. Molecular docking simulations corroborated these findings, revealing favorable binding energies between hexacyclinic acid and TNF-α (-8.62 kcal/mol) and IL-1β (-8.76 kcal/mol). These results suggest that hexacyclinic acid may exert its anti-osteoarthritis effects by modulating the IL-17 signaling pathway, particularly through interactions with TNF-α and IL-1β. The strong binding affinities observed indicate a potentially high efficacy of hexacyclinic acid in targeting these inflammatory mediators. These results have significant clinical implications, potentially leading to the development of new therapeutic strategies for osteoarthritis management with reduced side effects compared to current treatments. Future research should focus on experimental validation through in vitro and in vivo models to confirm these computational predictions and establish hexacyclinic acid as a viable candidate for clinical development
References
. Banerjee, P., Mandhare, A., & Bagalkote, V. (2022). Marine natural products as source of new drugs: an updated patent review (July 2018-July 2021). Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents, 32(3), 317–363. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543776.2022.2012150
Banday, A. H., Azha, N. ul, Farooq, R., Sheikh, S. A., Ganie, M. A., Parray, M. N., Mushtaq, H., Hameed, I., & Lone, M. A. (2024). Exploring the potential of marine natural products in drug development: A comprehensive review. Phytochemistry Letters, 59, 124–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2024.01.001
Höfs, R., Walker, M., & Zeeck, A. (2000). Hexacyclinic acid, a Polyketide from Streptomyces with a Novel Carbon Skeleton. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 39(18), 3258–3261. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3773(20000915)39:18<3258::AID-ANIE3258>3.0.CO;2-Q
Audic, A., & Prunet, J. (2022). Synthesis of the CDF Ring System of Hexacyclinic Acid. Synthesis (Germany), 55(15), 2333–2342. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-2022-1809
Stellfeld, T., Bhatt, U., & Kalesse, M. (2004). Synthesis of the A,B,C-Ring System of Hexacyclinic Acid. Organic Letters, 6(22), 3889–3892. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol048720o
Clarke, P. A., Grist, M., Ebden, M., & Wilson, C. (2003). Synthesis of a model DEF-ring core of hexacyclinic acid. Chem. Commun., 13, 1560–1561. https://doi.org/10.1039/B303706A
Clarke, P. A., Cridland, A. P., Rolla, G. A., Iqbal, M., Bainbridge, N. P., Whitwood, A. C., & Wilson, C. (2009). Studies on the Synthesis of the ABC Rings of (±)-Hexacyclinic Acid. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 74(20), 7812–7821. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo901547k
Clarke, P. A., Grist, M., Ebden, M., Wilson, C., & Blake, A. J. (2005). Synthetic studies on the DEF-rings of FR182877 and hexacyclinic acid. Tetrahedron, 61(2), 353–363. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2004.10.095
Gallo, K., Goede, A., Preissner, R., & Gohlke, B.-O. (2022). SuperPred 3.0: drug classification and target prediction—a machine learning approach. Nucleic Acids Research, 50(W1), W726–W731. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac297
Daina, A., Michielin, O., & Zoete, V. (2019). SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Research, 47(W1), W357–W3664. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz382
Szklarczyk, D., Kirsch, R., Koutrouli, M., Nastou, K., Mehryary, F., Hachilif, R., Gable, A. L., Fang, T., Doncheva, N. T., Pyysalo, S., Bork, P., Jensen, L. J., & von Mering, C. (2023). The STRING database in 2023: protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), D638–D646. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1000
Sherman, B. T., Hao, M., Qiu, J., Jiao, X., Baseler, M. W., Lane, H. C., Imamichi, T., & Chang, W. (2022). DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Research, 50(W1), W216–W221. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac194
Ge, S. X., Jung, D., & Yao, R. (2020). ShinyGO: a graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics, 36(8), 2628–2629. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz931
Lipinski, C. A. (2004). Lead- and drug-like compounds: the rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies, 1(4), 337–341. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2004.11.007
Pires, D. E., Blundell, T. L., & Ascher, D. B. (2015). pkCSM : predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic properties using graph-based signatures (Theory- How to Enterpret pkCSM Result). PKCSM, 5. http://biosig.unimelb.edu.au/pkcsm/theory
Loomis, T. A., & Hayes, A. W. (1996). CHAPTER 12 - Principles of Biological Tests for Toxicity. In T. A. Loomis & A. W. Hayes (Eds.), Loomis’s Essentials of Toxicology (Fourth Edition) (Fourth Edi, pp. 167–204). Academic Press. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012455625-6/50012-X
Kamiab, Z., Khorramdelazad, H., Kafi, M., Jafarzadeh, A., Mohammadi-Shahrokhi, V., Bagheri-Hosseinabadi, Z., Saeed Askari, P., & Abbasifard, M. (2024). Role of Interleukin-17 family cytokines in disease severity of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Advances in Rheumatology, 64(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-024-00351-5
Xiao, J., Zhang, P., Cai, F. L., Luo, C. G., Pu, T., Pan, X. L., & Tian, M. (2023). IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review. In Open Life Sciences (Vol. 18, Issue 1). Walter de Gruyter GmbH. https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2022-0747
Na, H. S., Park, J. S., Cho, K. H., Kwon, J. Y., Choi, J. W., Jhun, J., Kim, S. J., Park, S. H., & Cho, M. La. (2020). Interleukin-1-Interleukin-17 Signaling Axis Induces Cartilage Destruction and Promotes Experimental Osteoarthritis. Frontiers in Immunology, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00730
Molnar, V., Matišić, V., Kodvanj, I., Bjelica, R., Jeleč, Ž., Hudetz, D., Rod, E., Čukelj, F., Vrdoljak, T., Vidović, D., Starešinić, M., Sabalić, S., Dobričić, B., Petrović, T., Antičević, D., Borić, I., Košir, R., Zmrzljak, U. P., & Primorac, D. (2021). Cytokines and Chemokines involved in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Vol. 22, Issue 17). MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179208
Slovacek, H., Khanna, R., Poredos, P., Poredos, P., Jezovnik, M., Hoppensteadt, D., Fareed, J., & Hopkinson, W. (2021). Interrelationship of MMP-9, Proteoglycan-4, and Inflammation in Osteoarthritis Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis, 27. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029621995569
Mukherjee, A., & Das, B. (2024). The role of inflammatory mediators and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in the progression of osteoarthritis. Biomaterials and Biosystems, 13, 100090. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbiosy.2024.100090
Schuerwegh, A. J., Dombrecht, E. J., Stevens, W. J., Van Offel, J. F., Bridts, C. H., & De Clerck, L. S. (2003). Influence of pro-inflammatory (IL-1α, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4) cytokines on chondrocyte function. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 11(9), 681–687. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1063-4584(03)00156-0
Chen, B., Wang, L., Xie, D., & Wang, Y. (2024). Exploration and breakthrough in the mode of chondrocyte death - A potential new mechanism for osteoarthritis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 170, 115990. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115990
Estee, M., Cicuttini, F., Page, M., Wluka, A., & Wang, Y. (2023). Efficacy Of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors In Hand Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis Of Randomized Controlled Trials. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 31, S93–S94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2023.01.038
Magni, A., Agostoni, P., Bonezzi, C., Massazza, G., Menè, P., Savarino, V., & Fornasari, D. (2021). Management of Osteoarthritis: Expert Opinion on NSAIDs. In Pain and Therapy (Vol. 10, Issue 2, pp. 783–808). Adis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40122-021-00260-1
Timur, U. T., Caron, M. M. J., Jeuken, R. M., Bastiaansen-Jenniskens, Y. M., Welting, T. J. M., van Rhijn, L. W., van Osch, G. J. V. M., & Emans, P. J. (2020). Chondroprotective actions of selective COX-2 inhibitors in vivo: A systematic review. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Vol. 21, Issue 18, pp. 1–15). MDPI AG. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186962
Tu, M., Yang, M., Yu, N., Zhen, G., Wan, M., Liu, W., Ji, B., Ma, H., Guo, Q., Tong, P., Cao, L., Luo, X., & Cao, X. (2019). Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 activity in subchondral bone modifies a subtype of osteoarthritis. Bone Research, 7(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-019-0071-x
Bollmann, M., Pinno, K., Ehnold, L. I., Märtens, N., Märtson, A., Pap, T., Stärke, C., Lohmann, C. H., & Bertrand, J. (2021). MMP-9 mediated Syndecan-4 shedding correlates with osteoarthritis severity. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 29(2), 280–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2020.10.009
Meszaros, E., & Malemud, C. J. (2012). Prospects for treating osteoarthritis: Enzyme–protein interactions regulating matrix metalloproteinase activity. In Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease (Vol. 3, Issue 5, pp. 219–229). https://doi.org/10.1177/2040622312454157
Li, Z., Dai, A., Yang, M., Chen, S., Deng, Z., & Li, L. (2022). p38MAPK Signaling Pathway in Osteoarthritis: Pathological and Therapeutic Aspects. In Journal of Inflammation Research (Vol. 15, pp. 723–734). Dove Medical Press Ltd. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S348491
Fazio, A., Di Martino, A., Brunello, M., Traina, F., Marvi, M. V., Mazzotti, A., Faldini, C., Manzoli, L., Evangelisti, C., & Ratti, S. (2024). The involvement of signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: An update. Journal of Orthopaedic Translation, 47, 116–124. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jot.2024.06.002
Mushenkova, N. V., Nikiforov, N. G., Shakhpazyan, N. K., Orekhova, V. A., Sadykhov, N. K., & Orekhov, A. N. (2022). Phenotype Diversity of Macrophages in Osteoarthritis: Implications for Development of Macrophage Modulating Therapies. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Vol. 23, Issue 15). MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158381
Fernández Cuadros, M. E., Pérez Moro, O. S., Albaladejo Florín, M. J., Álava Rabasa, S., Lopez Munoz, M. J., & Rodríguez de Cía, J. (2021). A new paradigm for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: The role of hyaluronic acid, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and ozone in the modulation of inflammation: A review. In Revista de la Sociedad Espanola del Dolor (Vol. 28, Issue 5, pp. 282–291). Ediciones Doyma, S.L. https://doi.org/10.20986/resed.2021.3903/2021
Patil, R., Das, S., Stanley, A., Yadav, L., Sudhakar, A., & Varma, A. K. (2010). Optimized Hydrophobic Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding at the Target-Ligand Interface Leads the Pathways of Drug-Designing. PLOS ONE, 5(8), e12029-. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012029
Bonaventura, P., Lamboux, A., Albarède, F., & Miossec, P. (2018). Differential effects of TNF-α and IL-1β on the control of metal metabolism and cadmium-induced cell death in chronic inflammation. PLOS ONE, 13(5), e0196285-. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196285
He, M. M., Smith, A. S., Oslob, J. D., Flanagan, W. M., Braisted, A. C., Whitty, A., Cancilla, M. T., Wang, J., Lugovskoy, A. A., Yoburn, J. C., Fung, A. D., Farrington, G., Eldredge, J. K., Day, E. S., Cruz, L. A., Cachero, T. G., Miller, S. K., Friedman, J. E., Choong, I. C., & Cunningham, B. C. (2005). Small-Molecule Inhibition of TNF-α. Science, 310(5750), 1022–1025. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1116304
Vulpetti, A., Rondeau, J.-M., Bellance, M.-H., Blank, J., Boesch, R., Boettcher, A., Bornancin, F., Buhr, S., Connor, L. E., Dumelin, C. E., Esser, O., Hediger, M., Hintermann, S., Hommel, U., Koch, E., Lapointe, G., Leder, L., Lehmann, S., Lehr, P., … Hurth, K. (2024). Ligandability Assessment of IL-1β by Integrated Hit Identification Approaches. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 67(10), 8141–8160. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00240
Kurumbail, R. G., Stevens, A. M., Gierse, J. K., McDonald, J. J., Stegeman, R. A., Pak, J. Y., Gildehaus, D., iyashiro, J. M., Penning, T. D., Seibert, K., Isakson, P. C., & Stallings, W. C. (1996). Structural basis for selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by anti-inflammatory agents. Nature, 384(6610), 644–648. https://doi.org/10.1038/384644a0
Bissantz, C., Kuhn, B., & Stahl, M. (2010). A medicinal chemist’s guide to molecular interactions. In Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (Vol. 53, Issue 14, pp. 5061–5084). American Chemical Society. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm100112j
Zarghi, A., & Arfaei, S. (2011). Selective COX-2 Inhibitors: A Review of Their Structure-Activity Relationships. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 10, 655–683.
Oprea, T. I., Davis, A. M., Teague, S. J., & Leeson, P. D. (2001). Is There a Difference between Leads and Drugs? A Historical Perspective. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 41(5), 1308–1315. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci010366a
Leeson, P. D., & Springthorpe, B. (2007). The influence of drug-like concepts on decision-making in medicinal chemistry. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 6(11), 881–890. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2445
Pérez, M. A. C., Sanz, M. B., Torres, L. R., Avalos, R. G., González, M. P., & Díaz, H. G. (2004). A topological sub-structural approach for predicting human intestinal absorption of drugs. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 39(11), 905–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2004.06.012
Lin, J. H., & Yamazaki, M. (2003). Role of P-Glycoprotein in Pharmacokinetics. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 42(1), 59–98. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200342010-00003
Smith, D. A., Beaumont, K., Maurer, T. S., & Di, L. (2015). Volume of Distribution in Drug Design. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 58(15), 5691–5698. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00201
Issa, N. T., Wathieu, H., Ojo, A., Byers, S. W., & Dakshanamurthy, S. (2017). Drug Metabolism in Preclinical Drug Development: A Survey of the Discovery Process, Toxicology, and Computational Tools. Current Drug Metabolism, 18(6), 556–565. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389200218666170316093301
Durán-Iturbide, N. A., Díaz-Eufracio, B. I., & Medina-Franco, J. L. (2020). In Silico ADME/Tox Profiling of Natural Products: A Focus on BIOFACQUIM. ACS Omega, 5(26), 16076–16084. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01581
Hakkola, J., Hukkanen, J., Turpeinen, M., & Pelkonen, O. (2020). Inhibition and induction of CYP enzymes in humans: an update. In Archives of Toxicology (Vol. 94, Issue 11, pp. 3671–3722). Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02936-7
Zanger, U. M., & Schwab, M. (2013). Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: Regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation. In Pharmacology and Therapeutics (Vol. 138, Issue 1, pp. 103–141). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.12.007
Doogue, M. P., & Polasek, T. M. (2011). Drug dosing in renal disease. Clinical Biochemist Reviews, 32(2), 69–73. https://doi.org/10.5005/jp/books/12780_15
Paine, S. W., Barton, P., Bird, J., Denton, R., Menochet, K., Smith, A., Tomkinson, N. P., & Chohan, K. K. (2010). A rapid computational filter for predicting the rate of human renal clearance. Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling, 29(4), 529–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2010.10.003
Paine, S. W., Ménochet, K., Denton, R., McGinnity, D. F., & Riley, R. J. (2011). Prediction of human renal clearance from preclinical species for a diverse set of drugs that exhibit both active secretion and net reabsorption. Drug Metabolism and Disposition: The Biological Fate of Chemicals, 39(6), 1008–1013. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.110.037267
Hacker, K., Maas, R., Kornhuber, J., Fromm, M. F., & Zolk, O. (2015). Substrate-Dependent Inhibition of the Human Organic Cation Transporter OCT2: A Comparison of Metformin with Experimental Substrates. PloS One, 10(9), e0136451. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136451
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Arif Setiawansyah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license allows authors to use all articles, data sets, graphics, and appendices in data mining applications, search engines, web sites, blogs, and other platforms by providing an appropriate reference. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright without restrictions and will retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).





 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





