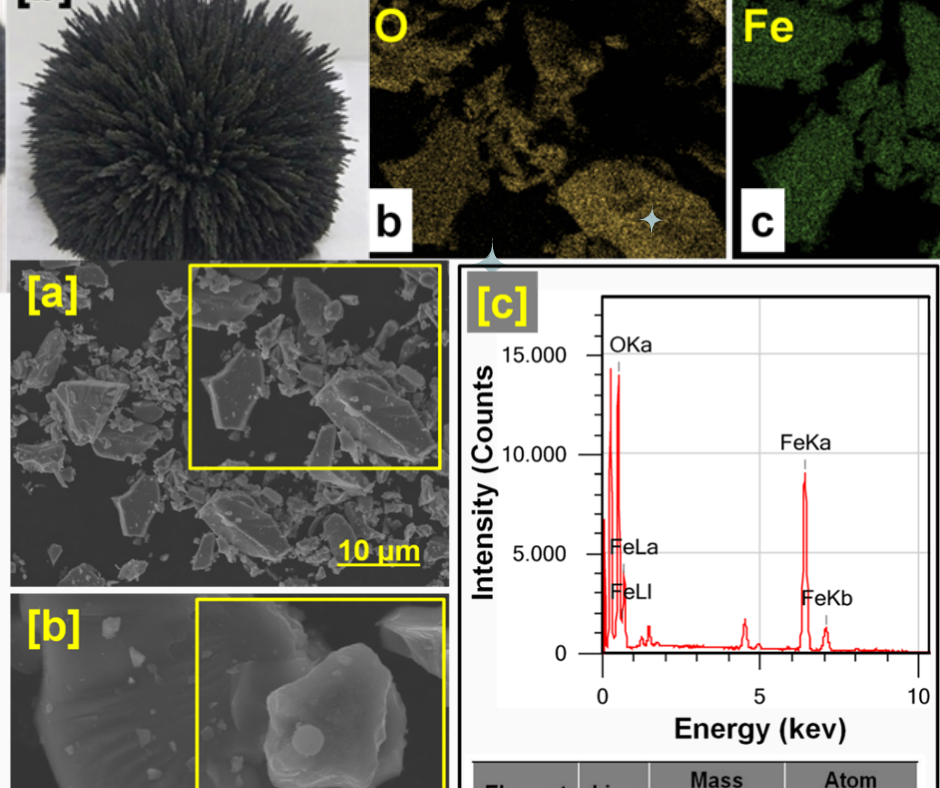
Free solvent isolation of Fe3O4 from magnetic material iron sand utilizing high-energy ball milling as adsorben remazol turquoise blue G-133 and remazol red RB-133
Published:
2023-02-18Issue:
Vol. 6 No. 1 (2023)Keywords:
adsorption, remazol, Ball-milling, Fe3O4, EquilibriumArticles
Downloads
How to Cite
Ramadhan, M., Fahmiati, F., Alrum, A., & La Ode Muhammad Zuhdi, M. (2023). Free solvent isolation of Fe3O4 from magnetic material iron sand utilizing high-energy ball milling as adsorben remazol turquoise blue G-133 and remazol red RB-133. Acta Chimica Asiana, 6(1), 269–278. Retrieved from https://aca.unram.ac.id/index.php/ACA/article/view/143
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Metrics
Metrics Loading ...






 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





