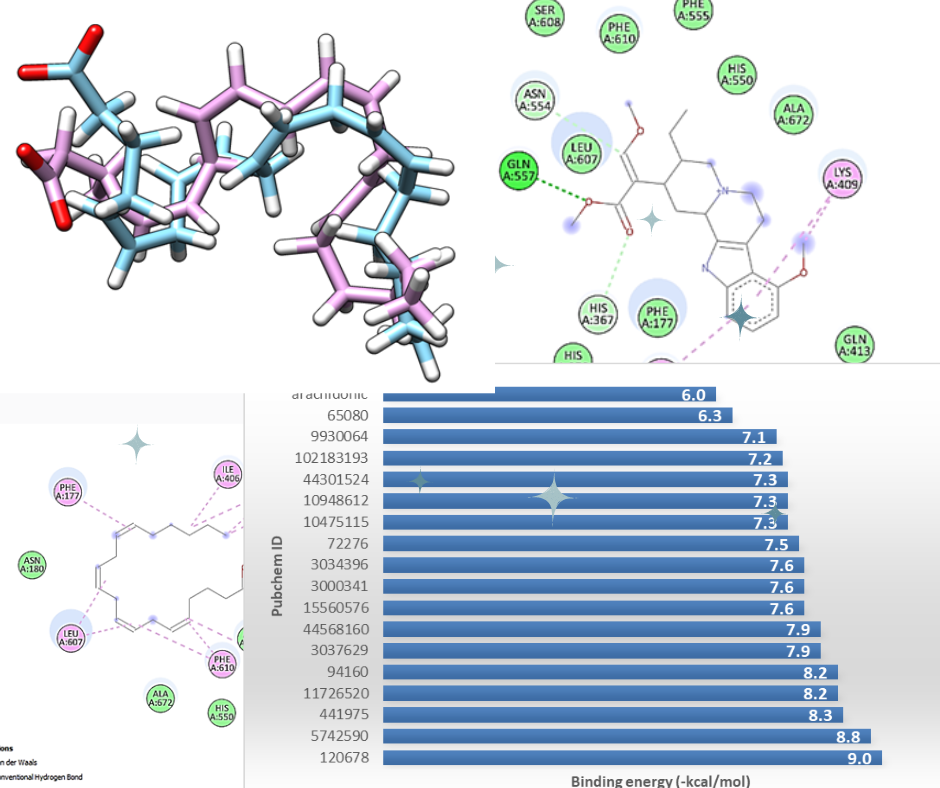
Identification of Active Compound from Mitragyna speciosa Leave as Antiinflammation Agent: In Silico Study.
DOI:
10.29303/aca.v5i2.139Published:
2022-12-31Issue:
Vol. 5 No. 2 (2022)Keywords:
Mitragyna speciose, antiinflammation, virtual screening, ADMETArticles
Downloads
How to Cite
Arief, I., & Kurnianto, E. (2022). Identification of Active Compound from Mitragyna speciosa Leave as Antiinflammation Agent: In Silico Study. Acta Chimica Asiana, 5(2), 218–223. https://doi.org/10.29303/aca.v5i2.139
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Metrics
Metrics Loading ...






 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





