Investigating Pt/Pumice catalyst for efficient 3-methyl-1-butanol conversion
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29303/aca.v7i2.162Keywords:
Modified Pt/pumice catalyst, conversion activity test, 3-methyl-1-butanolAbstract
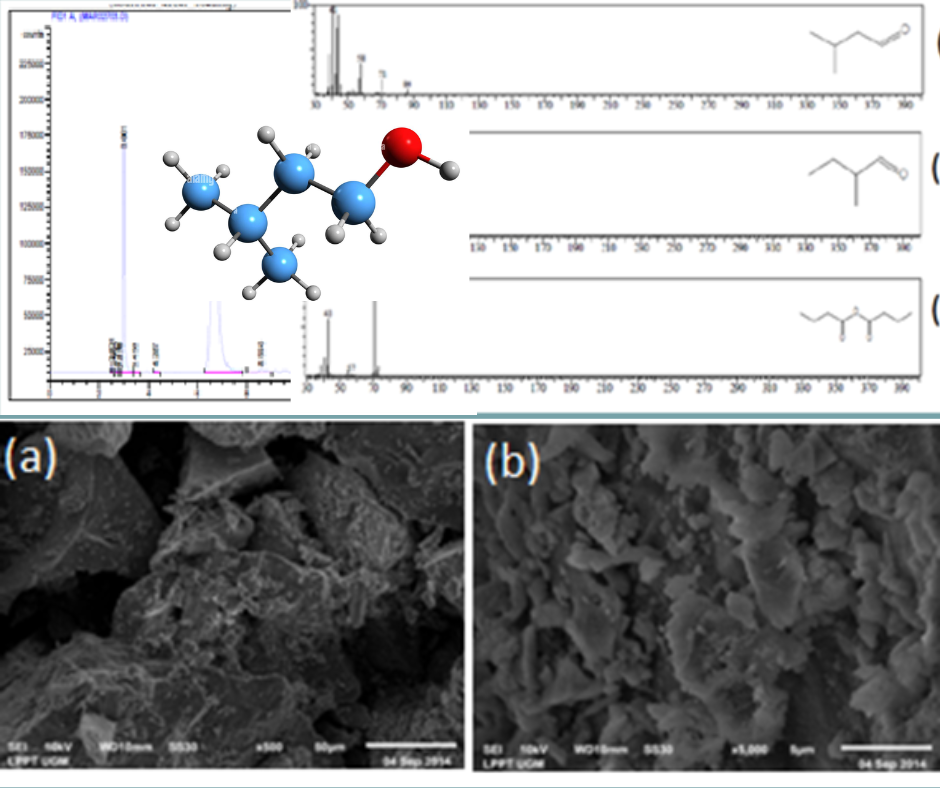
The objective of this study was to obtain a modified Pt/pumice catalyst to support the conversion reaction of 3-methyl-1-butanol under specific reaction conditions. To achieve this objective, the first step involved preparing modified pumice catalyst pellets by impregnating them with Pt metal followed by activation at a temperature of 500 °C. The second step involved characterizing the Pt/pumice catalyst, including the surface distribution of Pt metal using SEM. The third step involved conducting the catalyst activity test against 3-methyl-1-butanol in a reactor (furnace) at temperatures ranging from 400 to 500°C with a flow system for the feed. The fourth step involved analyzing the conversion results using GC-MS chromatograms. The research results showed that the Si/Al ratio in the modified Pt/Pumice catalyst using a PtCl4 solution with a concentration of 0.0321 M for impregnation was 4:1, compared to 4.8:1 for Pt/Zeolite and 3.2:1 for Pt/ABP. The modified catalyst activity test for 3-methyl-1-butanol showed the following conversion results: Pt/Pumice 27.63%, Pt/Zeolite 23.85%, Pt/Black Pumice 14.81%, and for platinum catalyst, the conversion was 22.35%. These results indicated that the highest conversion was observed in the treated sample A-3 under the reaction condition of 450°C. The conversion products analyzed using GC-MS showed the presence of three molecules: 3-methylbutanal, 2-methylbutanal, and anhydrous isobutanoate.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Sangeetha, S. P., Divahar, R., Mawlong, K., Lyngkhoi, B., & Kurkalang, A. (2020). Mechanical characteristics of pumice stone as light weight aggregate in concrete. International Journal of Science and Technology Research, 9(1), 3760–3762.
Babu, G. P., Murthy, R. S., & Krishnan, V. (1997). Conversion of isoamyl alcohol over acid catalysts: Reaction dependence on nature of active centers. Journal of Catalysis, 166(1).
Priatmoko, S., & Yahya, M. U. (2014). Optimasi dan studi kinetika reaksi konversi 3-metil 1-butanol menggunakan katalis Pt/zeolit alam.
Paputungan, M., & Triyono. (2000). Pengaruh etanol dan air pada reaksi konversi 3-metil-1-butanol dengan katalis Pt/zeolit dan Pt/asbes.
Paputungan, M. (2003). Karakteristik Batuan Aktif Gorontalo.
Paputungan, M. (2009). Karakterisasi Katalis Modifikasi Pd/Batuan Aktif.
Trianasari, T., Manurung, P., & Karo, P. K. (2017). Analisis dan karakterisasi kandungan silika (SiO₂) sebagai hasil ekstraksi batu apung (pumice). Jurnal Teori dan Aplikasi Fisika, 5(2), 179–186.
Knox, G. (1833). Experiments and observations on the neivry pitch-stone, and its products, and on the formation of pumice. Abstracts of the Papers Printed in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 2, 172.
Yucel, A., Efe, T., Onal, M., Depci, T., & Aydin, H. (2016). Mineralogical and chemical characterization of acidic pumices outcrop north of Lake Van. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 44, 052019.
Mardjan, M., Musa, W. J. A., & others. (2012). Analisis logam-logam pada batu apung dan modifikasinya serta uji adsorpsinya pada larutan asam asetat. Jurnal Sainstek, 6(05).
Nuari, F. H. S., Hendrawan, A. P., & Suprijanto, H. (2018). Evaluasi karakteristik permeabilitas dan ketahanan terhadap piping material piroklastik hasil erupsi Gunung Kelud tahun 2014 dan aplikasinya sebagai alternatif material timbunan. Universitas Brawijaya.
Aristantha, F., Hendrawan, A. P., & Asmaranto, R. (2017). Identifikasi karakteristik fisik dan mineralogi material piroklastik hasil erupsi Gunung Kelud di sungai Kali Sambong Desa Pandansari Kecamatan Ngantang Kabupaten Malang sebagai alternatif material timbunan. Jurnal Mahasiswa Jurusan Teknik Pengairan, 1(1).
Al-Shathr, A., Shakor, Z. M., Al-Zaidi, B. Y., Majdi, H. S., AbdulRazak, A. A., Aal-Kaeb, S., Shohib, A. A., & McGregor, J. (2022). Reaction kinetics of cinnamaldehyde hydrogenation over Pt/SiO₂: Comparison between bulk and intraparticle diffusion models. International Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022.
Ballarin, B., Gazzano, M., Scavetta, E., & Tonelli, D. (2009). One-step electrosynthesis of bimetallic Au-Pt nanoparticles on indium tin oxide electrodes: Effect of the deposition parameters. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 113(34), 15148–15154.
Örücü, E., Karakaya, M., Avcı, A. K., & Önsan, Z. I. (2005). Investigation of ethanol conversion for hydrogen fuel cells using computer simulations. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology: International Research in Process, Environmental & Clean Technology, 80(10), 1103–1110.
Kobayashi, S., Uchiyama, T., Kakinuma, K., Yamamoto, K., Matsunaga, T., Matsumoto, M., Imai, H., Sakurai, Y., Asaoka, T., Tsuji, Y., & others. (2022). Operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy of Pt catalyst in polymer electrolyte fuel cell under high temperature and low humidification. Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 242, 42, 1589.
Kuriganova, A., Faddeev, N., Gorshenkov, M., Kuznetsov, D., Leontyev, I., & Smirnova, N. (2020). A comparison of "bottom-up" and "top-down" approaches to the synthesis of Pt/C electrocatalysts. Processes, 8(8), 947.
Señorans, S., R-Díaz, J., Escalante, D., González, L. A., & Díaz, L. (2023). Ce/pumice and Ni/pumice as heterogeneous catalysts for syngas production from biomass gasification. Waste Management, 166, 270–279.
Liu, H., Zou, X., Chen, Q., Fan, W., & Gong, Z. (2022). Pumice-loaded rGO@MnO₂ nanomesh photocatalyst with visible light response for rapid degradation of ciprofloxacin. Separation and Purification Technology, 297, 121502.
Jalain, R., Bonnety, J., Legros, G., & Matynia, A. (2022). Doping rich ethylene premixed flames: Influence of C₃-C₅ alcohols on the structure of the steady one-dimensional laminar flame. Fuel, 307, 121793.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mardjan Paputungan, Akram La Kilo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license allows authors to use all articles, data sets, graphics, and appendices in data mining applications, search engines, web sites, blogs, and other platforms by providing an appropriate reference. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright without restrictions and will retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).







