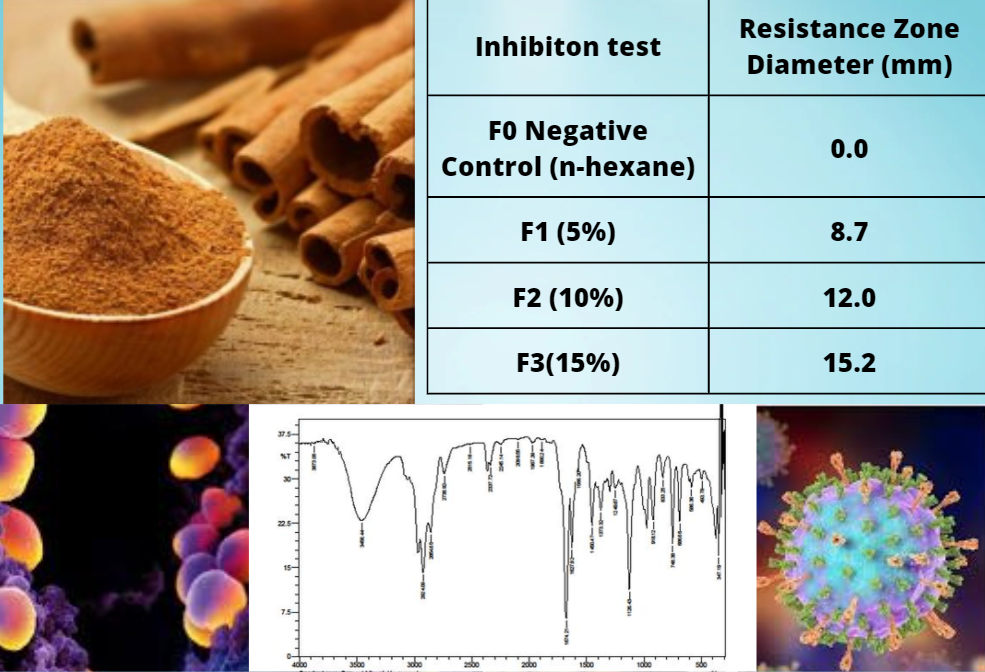
Cinnamon (Cinnamomum burmannii) Bark Essential Oil as Raw Material for Skin Cream and Anti-Bacterial
DOI:
10.29303/aca.v5i1.80Published:
2022-04-17Issue:
Vol. 5 No. 1 (2022)Keywords:
essential oil, cinnamon bark, face cream, antibacterialArticles
Downloads
How to Cite
Lewa, S., & Gugule, S. . (2022). Cinnamon (Cinnamomum burmannii) Bark Essential Oil as Raw Material for Skin Cream and Anti-Bacterial . Acta Chimica Asiana, 5(1), 158–165. https://doi.org/10.29303/aca.v5i1.80
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Metrics
Metrics Loading ...






 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





