Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum gratissimum root extract and their biological activities against some clinical pathogens
Authors
Chioma Mercy Nzerema , Prince Joe Nna , Kingsley John OrieDOI:
10.29303/aca.v8i2.267Published:
2025-11-28Issue:
Vol. 8 No. 2 (2025)Keywords:
Ocimum gratissimum, silver nanoparticles, green synthesis, antimicrobial activityArticles
Downloads
How to Cite
Downloads
Metrics
Abstract
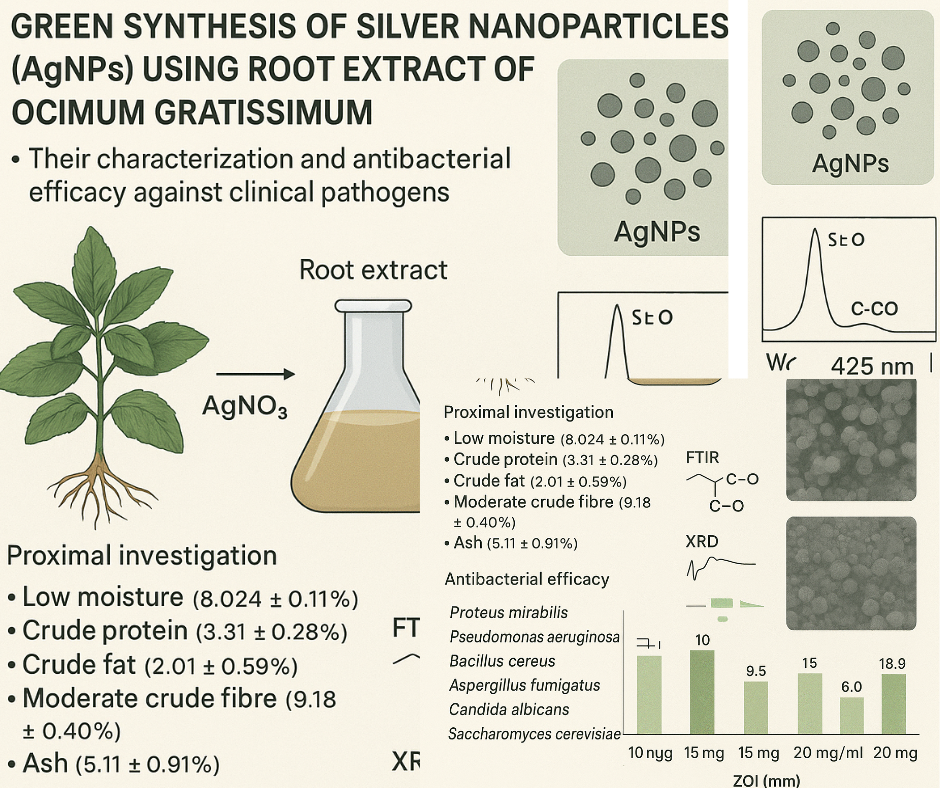
This study investigates the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Ocimum gratissimum root extract, along with their characterization and antibacterial efficacy. Proximal analysis revealed low moisture (8.02 ± 0.11%), crude protein (3.31 ± 0.28%), crude fat (2.01 ± 0.59%), moderate fibre (9.18 ± 0.40%), and ash (5.11 ± 0.91%), indicating a carbohydrate-rich composition. AgNPs were synthesized using the root extract as reducing and stabilizing agent; UV–Vis spectroscopy confirmed their formation with a surface plasmon resonance peak at 425 nm, consistent with spherical nanoparticles (30–100 nm). FTIR identified phenolic and polysaccharide functional groups (O–H, C=O, C–O), while XRD indicated a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure with good crystallinity. SEM micrographs showed mostly spherical particles with minimal aggregation. Antimicrobial activity at 10–20 mg/mL was tested against Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus fumigatus, Candida albicans, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The root extract alone showed no activity at 10 mg/mL but exhibited dose-dependent inhibition at higher concentrations (ZOIs: 10.40–15.16 mm). AgNPs displayed stronger broad-spectrum efficacy (ZOIs: 7.12–18.9 mm), often surpassing gentamicin. These findings highlight the potential of O. gratissimum root-derived AgNPs as eco-friendly antibacterial agents against multidrug-resistant organisms.
References
Tabor, A., & Jufar, D. (2024). Green-synthesised silver nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and alternative mechanisms of action to combat multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens: a systematic literature review. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 17(1), 2412601.
Elbehiry, A., & Abalkhail, A. (2025). Antimicrobial Nanoparticles Against Superbugs: Mechanistic Insights, Biomedical Applications, and Translational Frontiers. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1195.
Sharma, K., Guleria, S., & Razdan, V. K. (2019). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum gratissimum leaf extract: characterization, antimicrobial activity and toxicity analysis. Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 28(4), 519–525.
WHO. (2020). Antimicrobial resistance: Global report on surveillance. World Health Organization.
Orie, K. J., & Okocha, B. I. (2024). Biosynthesis and antimicrobial studies of zinc oxide nanoparticles of Vernonia amygdalina Leaf with varying concentration of zinc oxide. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 162, 112178.
Liao, S., Zhang, Y., Pan, X., Zhu, F., Jiang, C., Liu, Q., ... & Chen, L. (2019). Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International journal of nanomedicine, 1469-1487.
Sharma, K., Guleria, S., & Razdan, V. K. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum gratissimum leaf extract: characterization, antimicrobial activity and toxicity analysis. Journal of plant biochemistry and biotechnology, 29, 213-224.
Prabhu, K. S., Lobo, R., Shirwaikar, A. A., & Shirwaikar, A. (2009). Ocimum gratissimum: A review of its chemical, pharmacological and ethnomedicinal properties. The Open Complementary Medicine Journal, 1(1), 1-15.
George, I. E., Cherian, T., Ragavendran, C., Mohanraju, R., Dailah, H. G., Hassani, R., & Mohan, S. (2023). One-pot green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using brittle star Ophiocoma scolopendrina: Assessing biological potentialities of antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-diabetic and catalytic degradation of organic dyes. Heliyon, 9(3).
AOAC. (2005). Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International (18th ed.). Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
Okocha, B. I., Orie, K. J., Duru, R. U., & Ngochindo, R. L. (2023). Analysis of the active metabolites of ethanol and ethyl acetate extract of Justicia carnea. African Journal of Biomedical Research, 26(1), 109-117.
Thakur, A., Verma, M., Bharti, R., & Sharma, R. (2023). Recent advancement in the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Current Chinese Science, 3(5), 322-348.
Nna, P. J., Baride, N., & Orie, K. J. (2025). Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties of Metal-based Tosylamides. Faculty of Natural and Applied Sciences Journal of Applied Chemical Science Research, 2(2), 76-81.
Sharma, A., Madhu, Kondalkar, S. A., Meena, A. K., & Upadhyay, S. K. (2024). Herbal Nutraceutical as Alternative Medicine. Herbal Nutraceuticals: Products and Processes, 23-45.
Lee, B., Lee, M. J., Yun, S. J., Kim, K., Choi, I. H., & Park, S. (2019). Silver nanoparticles induce reactive oxygen species-mediated cell cycle delay and synergistic cytotoxicity with 3-bromopyruvate in Candida albicans, but not in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 4801-4816.
Orie, K. J., & Okocha, B. I. (2024). In vitro Anti-microbial and free radical scavenging activity of Zinc (II), Copper (II), Cobalt (II) and Cadmium (II) Ions Coordinated with N-(pyridin-4-yl)(tolu-4-yl) sulphonamide. African Journal of Biomedical Research, 27(2), 349-357.
Jyoti, K., Baunthiyal, M., & Singh, A. (2016). Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Urtica dioica Linn. leaves and their synergistic effects with antibiotics. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 9(3), 217-227.
Iravani, S. (2011). Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green chemistry, 13(10), 2638-2650.
Ahmed, S., Ahmad, M., Swami, B. L., & Ikram, S. (2016). A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. Journal of advanced research, 7(1), 17-28.
Awote, O. K., Ojekale, A. B., Kazeem, M. I., Adeyemo, A. G., Igbalaye, J. O., Ilesanmi, R., ... & Salako, D. S. (2024). Antidiabetic, antioxidant, antiglycation, and anti-inflammatory potentials of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles using Telfairia occidentalis leaf and stem aqueous extracts. Letters in Appl. NanoBioSci, 13(1), 41.
Javed, M. A., Ali, B., Sarfraz, M. H., Ali, S., Liaqat, E., Afzal, M. S., ... & Elshikh, M. S. (2024). Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential. Green Processing and Synthesis, 13(1), 20230248.
Restrepo, C. V., & Villa, C. C. (2021). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles, influence of capping agents, and dependence on size and shape: A review. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 15, 100428.
Singh, H., Desimone, M. F., Pandya, S., Jasani, S., George, N., Adnan, M., ... & Alderhami, S. A. (2023). Revisiting the green synthesis of nanoparticles: uncovering influences of plant extracts as reducing agents for enhanced synthesis efficiency and its biomedical applications. International journal of nanomedicine, 4727-4750.
Nna, P. J., Legborsi, J., & Orie, K. J. (2020). Comparative Study on the Phytoconstituents and Antimicrobial Analysis of Jatropha curcas Leaf and Stem Bark. Direct Res. J. Chem. Mater. Sci, 7(3), 37-43.
Hashem, A. H., Saied, E., Badr, B. M., Dora, M. S., Diab, M. A., Abdelaziz, A. M., ... & Attia, M. S. (2025). Biosynthesis of trimetallic nanoparticles and their biological applications: a recent review. Archives of Microbiology, 207(3), 1-35.
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Chioma Mercy Nzerema, Prince Joe Nna, Kingsley John Orie

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license allows authors to use all articles, data sets, graphics, and appendices in data mining applications, search engines, web sites, blogs, and other platforms by providing an appropriate reference. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright without restrictions and will retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in ACA: Acta Chimica Asiana.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).





 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





