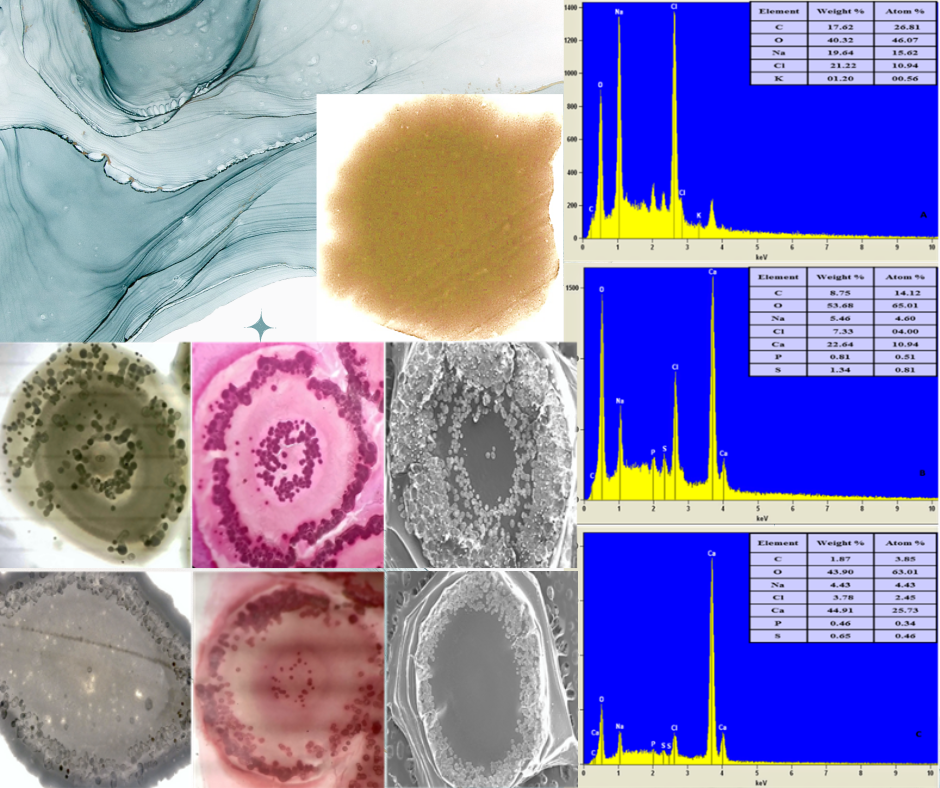
Effect of Different Calcium Salts on Calcium Carbonates Formation Induced by Halophilic Bacillus oceanisediminis CB1
DOI:
10.29303/aca.v5i2.138Published:
2022-12-31Issue:
Vol. 5 No. 2 (2022)Articles
Downloads
How to Cite
Bhagat, C. ., Bhavsar, S. ., Patel, R., Ghelani, A. ., Dudhagara, P., & Chaudhari, R. . (2022). Effect of Different Calcium Salts on Calcium Carbonates Formation Induced by Halophilic Bacillus oceanisediminis CB1. Acta Chimica Asiana, 5(2), 212–217. https://doi.org/10.29303/aca.v5i2.138
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Metrics
Metrics Loading ...






 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





