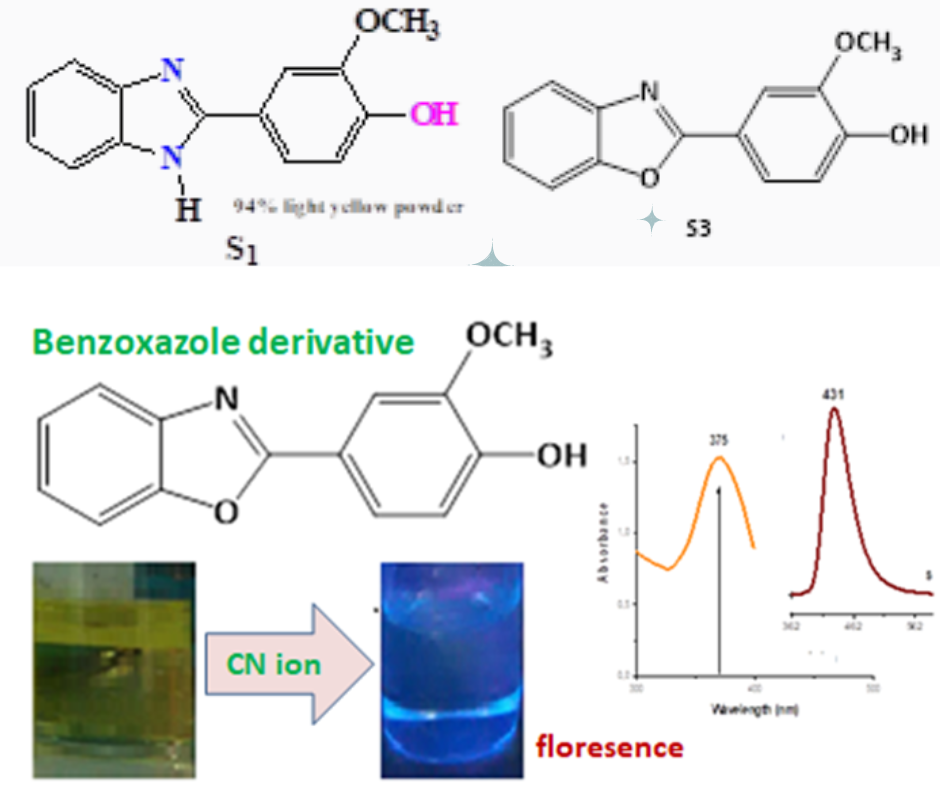
Effect of oxygen heteroatom on sensor-cyanide anions binding
DOI:
10.29303/aca.v5i2.118Published:
2022-12-23Issue:
Vol. 5 No. 2 (2022)Keywords:
oxygen, heteroatom, anions, sensorArticles
Downloads
How to Cite
Rahmawati, R., & Sofia, F. D. . (2022). Effect of oxygen heteroatom on sensor-cyanide anions binding . Acta Chimica Asiana, 5(2), 208–211. https://doi.org/10.29303/aca.v5i2.118
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Metrics
Metrics Loading ...






 Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
Indonesian Chemical Society, Chapter Nusa Tenggara. Jalan Majapahit 62 Mataram, University of Mataram, 83125, Indonesia





